Introduction
If falling asleep feels harder than it should, you’re not alone.
Many people can make it through the day exhausted, only to lie awake at night with a brain that refuses to slow down. For some, it’s racing thoughts. For others, it’s physical restlessness, stress, or the feeling of being “tired but wired.” And after trying multiple supplements that either don’t work or cause next-day grogginess, frustration sets in fast.
The problem isn’t a lack of options — it’s too many conflicting ones.
Melatonin doses vary wildly. Herbal blends promise miracles. Online advice contradicts itself. And trial-and-error becomes expensive and discouraging.
The truth is, falling asleep faster isn’t about finding a stronger pill. It’s about supporting the specific biological systems that allow sleep to begin naturally.
In this guide, we’ll break down 7 science-backed natural ingredients shown to help the body shift into sleep more easily — without forcing sedation. These are ingredients often discussed when people search for the best natural sleep aid, but rarely explained clearly or honestly.
Important Guidelines: 7 Natural Ingredients That Help You Fall Asleep Faster
Each of the ingredients below works in a different way, which is why no single supplement works for everyone. Understanding how they work helps you choose smarter — and avoid wasting money.
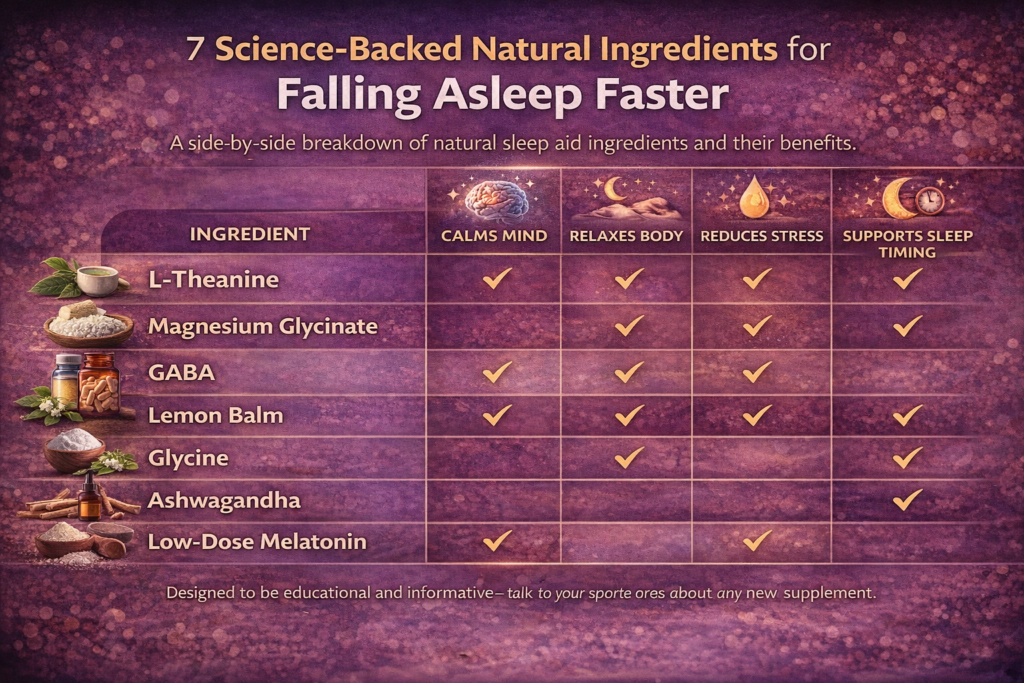
1. L-Theanine — For Quieting Racing Thoughts
L-Theanine is a natural compound found in green tea and has been studied for its potential to promote calmness without causing sedation. It influences the production of alpha brain waves, which are associated with a meditative, relaxed state. By modulating these brain waves, L-Theanine helps your mind achieve a calmer baseline, making it easier to shift into sleep.
Why it helps you fall asleep faster:
- Reduces mental chatter
- Calms stress-related alertness
- Doesn’t cause drowsiness or fog
This makes L-Theanine especially useful for:
- Parents whose minds replay the day at night
- Professionals who struggle to “switch off.”
- Shift workers relaxing following irregular hours.
Unlike sleep medications, it doesn’t force sleep — it removes one of the biggest barriers to falling asleep: overactive thinking.
👉 Learn how L-Theanine promotes natural sleep
2. Magnesium Glycinate — For Physical Relaxation
Magnesium is essential for regulating the nervous system and enabling muscle relaxation. Magnesium glycinate, a form gentle on digestion, supports enzymes involved in producing calming neurotransmitters and helps reduce muscle electrical activity. This allows your body to physically relax, easing the shift into sleep.
Why it helps:
- Relaxes muscles and nerves
- Supports GABA activity (a calming neurotransmitter)
- Helps the body shift out of “stress mode.”
Low magnesium levels are common in adults dealing with chronic stress, disrupted sleep schedules, or poor recovery.
This ingredient is often helpful for people who feel physically tense at bedtime rather than mentally overstimulated.
3. GABA — For Nervous System Calm
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a neurotransmitter that slows brain activity by binding to specific receptors, indicating to the nervous system to relax. When GABA activity is insufficient, the brain stays alert, preventing restful sleep.
When GABA signaling is low or inefficient, the brain stays in an alert, reactive state — even when you’re exhausted.
Why does it help with sleep onset?
- Reduces excitatory brain activity
- Supports soothing without heavy sedation
- Assists in signaling safety to the nervous system
GABA is especially relevant for people who experience:
- Bedtime anxiety
- Restlessness
- Difficulty staying relaxed once in bed
👉See how GABA-supporting ingredients help calm the brain before sleep
4. Lemon Balm — For Stress-Related Sleeplessness
Lemon balm is an herb historically used for reducing stress. It interacts with brain receptors tied to anxiety and supports mild increases in GABA levels, promoting a calming effect. This gentle mechanism makes it better tolerated than strong sedatives, as it calms the nervous system gently.
Benefits include:
- Reduced stress and nervous tension
- Mild support for GABA activity
- Calming effects without next-day grogginess
It’s particularly helpful when sleep problems are tied to emotional stress rather than circadian rhythm disruption.
5. Glycine — For Body Temperature Regulation
Glycine is an amino acid that assists in regulating core body temperature—a vital signal for sleep onset. By promoting peripheral blood flow, glycine helps lower body temperature, which triggers the natural sleep process.
Glycine helps support that process.
Why it helps:
- Promotes faster sleep onset
- May improve sleep efficiency
- Doesn’t act as a sedative
This makes it a useful option for people who:
- Feel “warm” or restless at night.
- Have trouble settling physically
- Want support without aggressively altering brain chemistry.
6. Ashwagandha — For Stress Hormone Balance
Ashwagandha is an adaptogen that helps modulate cortisol, a key stress hormone. It acts on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis to reduce excessive cortisol production, lowering your body’s stress response so you can relax more easily at night.
Elevated cortisol at night is a common — and often overlooked — reason people can’t fall asleep.
Why it helps:
- Supports stress resilience
- Helps lower nighttime cortisol
- Supports relaxation over time
This ingredient works best when used consistently, not as a one-night fix.
👉 Understand how stress hormones interfere with sleep — and how to calm them naturally
7. Low-Dose Melatonin (When Used Correctly)
Melatonin is a hormone that signals the body to begin the sleep process. When used in low doses and at the right times, melatonin supplements strengthen the body’s natural sleep signal rather than simply causing sedation. Misuse—like high doses or improper timing—disturbs this signal and causes side effects.
High doses can cause drowsiness, vivid dreams, or effects similar to dependence. But low doses, timed properly, can help signal sleep onset — especially for shift workers or travelers.
Best use cases:
- Jet lag
- Circadian rhythm misalignment
- Occasional schedule disruptions
Melatonin should be treated as a timing signal, not a knockout pill.
Advanced Strategies: How Ingredients Work Best Together
Here’s what many people miss:
The effectiveness of any ingredient depends on what’s keeping you awake.
Falling asleep faster usually requires:
- Calming the mind
- Relaxing the body
- Reducing stress signaling
- Supporting natural sleep timing
- A trending example of the quick-fix mindset
That’s why well-designed formulas combine multiple complementary ingredients rather than relying on one.
👉See how multi-ingredient sleep strategies outperform single supplements
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
1. Chasing Stronger Doses
More isn’t better. Stronger often leads to tolerance or side effects.
2. Expecting Instant Results
Some ingredients support sleep gradually, not overnight.
3. Ignoring Root Causes
Supplements won’t override chronic stress, inflammation, or circadian disruption.
4. Switching Products Too Quickly
Frequent changes prevent your body from adapting properly.
Expert Advice: How to Choose Smarter
When evaluating any natural sleep support, ask:
- Does this calm the nervous system or force sedation?
- Are doses reasonable and transparent?
- Is it designed to help you fall asleep, or just “make you drowsy”?
There is no universal best natural sleep aid — only the best suited sleep aid for your biology and sleep challenges.
👉 Follow the complete sleep journey to understand what your body actually needs
Conclusion
Falling asleep faster isn’t about overpowering the brain — it’s about creating the conditions where sleep can happen naturally.
The ingredients covered here are supported by research, widely used, commonly used, and typically well-accepted. But their real power comes from using them intentionally, not blindly.
When you understand why you’re struggling to fall asleep, you stop wasting money on trial-and-error — and start choosing solutions that actually work with your body.
Better sleep doesn’t come from chasing stronger supplements.
It comes from working with your biology.
