Insomnia doesn’t usually start with a broken ability to sleep.
It starts with a few bad nights — and the moment you begin worrying about them.
You’re exhausted, your body clearly wants rest, but the second your head hits the pillow your mind switches on. You start watching the clock. You calculate how many hours you might still get. You tell yourself this night has to be different — and suddenly sleep feels further away than ever.
That cycle is not a failure of willpower or discipline. It’s a learned response. And once it’s understood, it can be reversed.
This guide is written for beginners who want to treat insomnia without medication dependence, extreme routines, or trying harder at bedtime. Instead of chasing sleep, you’ll learn how insomnia actually persists — and how proven, evidence-based approaches help you treat insomnia naturally.
🎥 Before understanding insomnia, most people believe:
- Trying harder will eventually make sleep happen
- Lying in bed longer increases the chance of sleeping
- Controlling sleep is the solution
The result?
- More pressure at bedtime
- A racing mind
- Heightened frustration
- Sleep becoming something you fight instead of something that happens naturally
The harder you try, the more alert your brain becomes.
After understanding why sleep effort backfires from this video.
- You stop forcing sleep
- Bedtime pressure decreases
- The nervous system begins to calm
- Sleep becomes less of a struggle
Instead of chasing sleep, you create the conditions that allow it to return naturally.
Not through willpower — but through reducing effort and stress.
Why Insomnia Feels So Hard to Break
Insomnia and anxiety reinforce each other:
- You can’t sleep
- You worry about not sleeping
- Worry activates the nervous system
- Sleep becomes harder
Over time, your brain starts to associate bedtime with alertness instead of rest. For many, simply getting into bed triggers tension.
This doesn’t mean anything is wrong with you. It means your nervous system learned a pattern. Your biggest obstacle, calming your nervous system, matters more than forcing sleep.
🌙 The 12-Minute Insomnia Cure Is Trending — But Does It Really Work?
The Four Main Types of Insomnia
Insomnia usually appears in one or more of these forms.
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Difficulty staying asleep
- Waking too early and not returning to sleep
- Night Shift Workers sleep patterns
Short-term insomnia after stress is normal. The issue arises when short-term sleep trouble becomes chronic, often because well-intentioned coping strategies backfire.
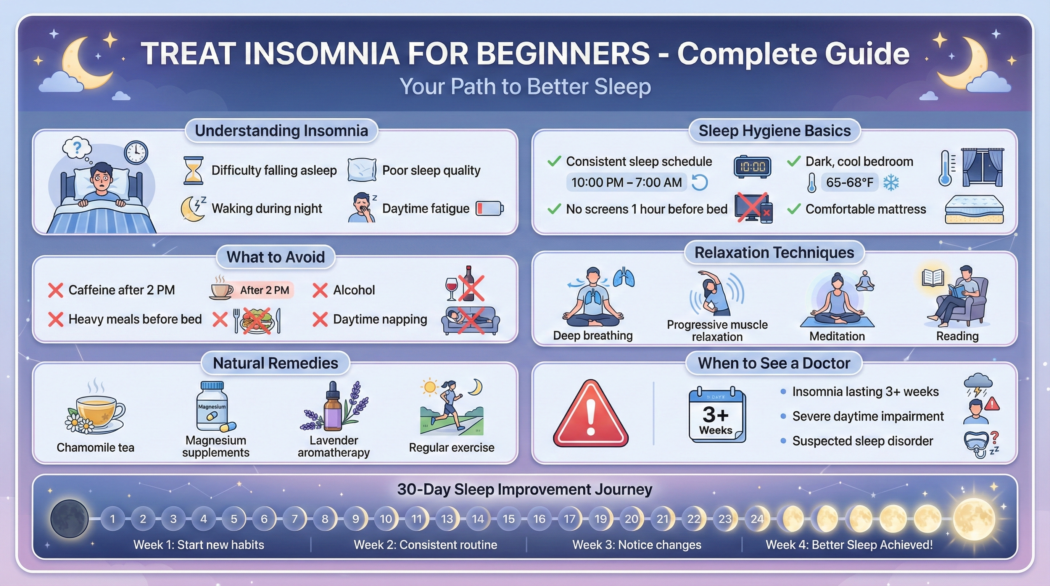
How Insomnia Becomes Chronic
When sleep feels unreliable, people often try to “fix” it by:
- Going to bed earlier
- Sleeping in on weekends
- Taking naps
- Increasing caffeine
- Reducing evening activity
- Drinking more alcohol
These behaviors weaken sleep drive and disrupt circadian rhythm. The real solution starts with your gut health and how your gut sends sleep signals to your brain.
At the same time, people start monitoring sleep closely: clock-watching, calculating hours, judging when to sleep at night. This hyper-focus keeps the brain alert.
This is why insomnia often persists even when you’re doing “everything right.”
🧠 Why Sleep Aids Stop Working And What Actually Fixes Chronic Insomnia
The Gold Standard Treatment: CBT-I
The most effective long-term treatment for chronic insomnia is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I).
CBT-I outperforms sleep medication in long-term studies and is recommended as the first-line treatment by major medical organizations.
It works by addressing:
- Sleep behaviors
- Sleep anxiety
- Conditioned arousal
Most people notice improvement within weeks.
Many CBT-I-based plans also integrate gentle, non-habit-forming sleep support when appropriate.
Sleep Restriction: Why Less Time in Bed Helps
Sleep restriction means temporarily limiting time in bed to match how much you’re actually sleeping.
Instead of lying awake for hours, you build strong sleep pressure so your brain stops fighting sleep. This often leads to:
- Faster sleep onset
- Fewer awakenings
- Deeper sleep
The first week can be uncomfortable, but most people improve quickly.
This approach works best when you understand why less restorative sleep is safe — and why your body will sleep without force.
👉 Why You Wake Up at the Same Time Every Night
Stimulus Control: Re-Training Your Brain
Use your bed only for sleep and relaxation.
Key rules:
- Go to bed only when sleepy.
- No scrolling or worrying in bed
- If awake ~20 minutes, get up.
This trains your brain to associate bed with sleep instead of frustration.
How Thoughts About Sleep Keep You Awake
Common sleep-blocking thoughts include:
- “I need 8 hours or tomorrow is ruined.”
- “I’ll never sleep normally again.”
- “Something is wrong with me.”
These thoughts cause performance anxiety. The thought that imperfect sleep is safe — and temporary — often reduces insomnia dramatically.
Understanding these mental patterns is often enough to reduce nighttime anxiety.
👉 How to Sleep Longer Than 6 Hours: Proven, Science-Backed Strategies That Actually Work
Supporting Sleep Biology (Without Medication Dependence)
Strong sleep comes from working with your biology:
- Consistent wake time
- Morning light exposure
- Daytime movement
- Reduced evening light
- Cool bedroom temperature
Supplements can support this foundation when used properly.
If you’re unsure whether melatonin or magnesium makes sense for you, this breakdown helps.
👉 Beyond Melatonin: Stronger Herbal and Supplement-Based Sleep Aids
Where Supplements Fit (and Where They Don’t)
Supplements don’t fix insomnia, but they can support sleep when anxiety and circadian disruption are involved.
Magnesium may help:
- Calm the nervous system.
- Reduce nighttime tension
Melatonin works best for:
- Circadian rhythm issues
- Travel or schedule disruption
For brand-specific guidance and safety considerations, see our full breakdown.
👉 Complete Guide to Nature Made Products and Services
Middle-of-the-Night Wake-Ups
Brief awakenings are normal. Problems begin when waking becomes stressful. Helpful rules:
- Avoid clock-watching
- Get out of bed if fully alert
- Keep lights dim, avoid blue light
- Avoid stimulation
Alcohol, late caffeine, and blood-sugar drops can worsen night awakenings.
When Standard Approaches Aren’t Enough
Persistent insomnia may involve:
- Sleep apnea or restless legs
- Hormonal changes
- Chronic pain
- Mental health conditions
- Medication side effects
These require targeted evaluation along with insomnia treatment.
🌙 The Definitive List of Doctor-Recommended Natural Sleep Ingredients
Key Takeaways for Beginners
- Insomnia is learned — and reversible.
- CBT-I works better than medication long-term
- Less time in bed can mean better sleep.
- Anxiety maintains insomnia
- Consistency beats perfection
If you want to support your sleep without prescription drugs or habit-forming aids, many beginners start with gentle, non-sedating tools designed specifically for insomnia and nighttime anxiety.
YuSleep is built around evidence-based sleep principles — not quick fixes. YuSleep is designed for people whose insomnia is driven by anxiety, racing thoughts, and sleep pressure — not chemical dependency.
