Sleep aids often work at first — and then suddenly don’t.
If you’ve ever thought, “This used to knock me out… why am I awake again?” you’re not imagining it.
This is one of the most common patterns in chronic insomnia.
The reason sleep aids stop working isn’t willpower or tolerance alone — it’s that they don’t tackle the fundamental reasons behind poor sleep.
This guide explains:
- Why sleep aids lose effectiveness
- The biological reasons for insomnia becoming persistent.
- What actually restores deep, steady sleep long-term
🎥 If sleep aids worked for you at first and then stopped, this short video explains why.
Most people assume they’ve built tolerance — but the real issue is usually deeper. In this video, we break down the biological reasons sleep aids lose effectiveness and why insomnia becomes persistent over time.
Below, we’ll go deeper into why this happens, the most common reasons sleep aids stop working, and what actually restores deep, consistent sleep long term.
Why Do Sleep Aids Stop Working? ✅
Sleep aids stop working because the body adapts to them, while the underlying causes of insomnia — such as nervous system hyperarousal, hormonal disruption, and circadian misalignment — remain unresolved.
Over time, this leads to:
- Weakened effect
- Rebound insomnia
- Dependence on higher doses or combinations
The 5 Main Reasons Sleep Aids Lose Effectiveness
1️⃣ Tolerance Builds Quickly
Many sleep aids — including melatonin and sedating supplements — lose effectiveness as the brain adapts.
Your body strives for balance. When an external sleep signal is introduced repeatedly, the brain often downregulates its own sleep signaling.
Result: You need more to feel the same effect — or nothing happens at all.
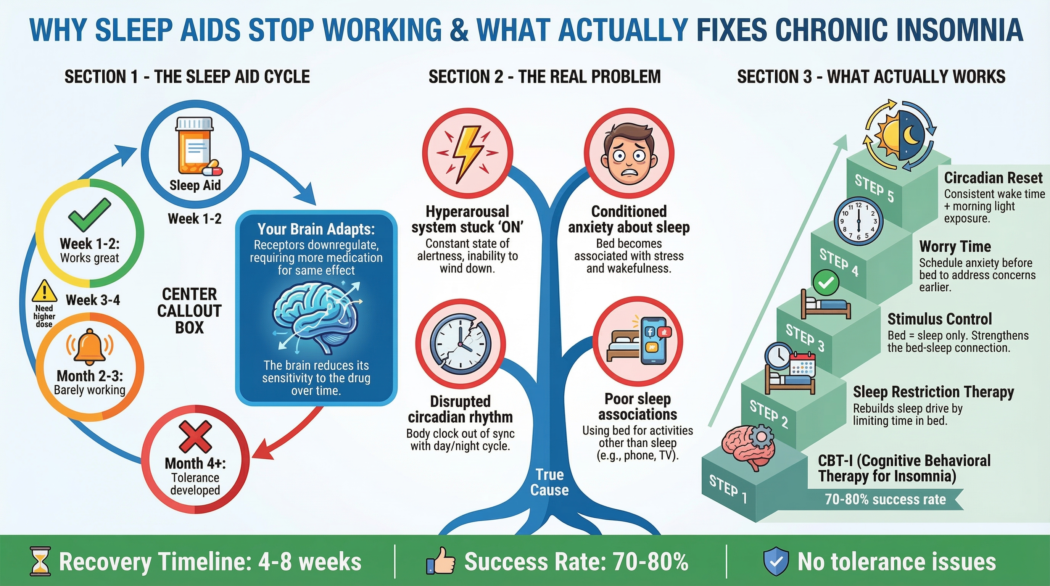
2️⃣ They Don’t Calm the Nervous System
Most sleep aids focus on sedation rather than regulation.
If your nervous system is stuck in fight-or-flight (stress, anxiety, burnout), no amount of “sleep pressure” will override that state.
This is why people feel:
- Tired but wired
- Fatigued yet alert
- Calm during the day, restless at night
3️⃣ Cortisol Overrides Sleep Signals
Even strong sleep aids can’t compete with elevated cortisol.
If stress hormones rise at night — common with chronic stress, overtraining, or shift work — they block sleep initiation and maintenance, regardless of what you take.
4️⃣ Circadian Rhythm Is Misaligned
Sleep aids do not reset your internal clock.
If your circadian rhythm is disrupted (night shifts, late light exposure, inconsistent wake times), sleep aids may help temporarily — but the timing of sleep remains unstable.
This leads to:
- Early awakenings
- Interrupted sleep
- Non-restorative rest
5️⃣ They Treat Symptoms, Not Causes
Sleep aids mask insomnia — they don’t fix it.
They don’t address:
- Autonomic nervous system imbalance
- Stress-response conditioning
- Hormonal timing
- Sleep anxiety loops
Without dealing with these, insomnia returns the moment the aid loses potency.
Signs a Sleep Aid Is No Longer Helping
- You fall asleep but wake up too early.
- Sleep feels light or broken.
- Anxiety increases when you don’t take it.
- You rotate products hoping something “works again.”
These are signals, not shortcomings.
What Actually Fixes Chronic Insomnia (Long-Term)
Lasting sleep improvement comes from restoring regulation, not forcing sleep.
The most effective strategies focus on:
- Nervous system downshifting
- Cortisol rhythm normalization
- Circadian alignment
- Removing conditioned arousal around sleep
👉 What Actually Fixes Chronic Insomnia
Where Sleep Aids Can Still Help (When Used Correctly)
Sleep aids aren’t useless — they’re just often misused.
They can be helpful:
- As short-term support during stress
- When paired with circadian and nervous system work
- When non-habit-forming and non-sedating
The key is to support calm, not knock yourself out.
If stress, anxiety, or a “wired-but-tired” feeling keeps you awake, sleep aids alone often stop working because the nervous system never fully downshifts.
In those cases, targeted, non-melatonin sleep support designed to promote nighttime calm — rather than force sedation — can help the body respond to relaxation techniques again.
👉 View the sleep support I recommend for nervous-system–driven insomnia
Sleep Aids vs Root-Cause Sleep Repair
| Traditional sleep aids | ✅ | ❌ |
| Higher doses | ⚠️ | ❌ |
| Nervous system regulation | ✅ | ✅ |
| Circadian alignment | ✅ | ✅ |
| Behavioral + physiological support | ✅ | ✅ |
FAQs About Sleep Aids and Insomnia
Why do sleep aids work at first?
They temporarily override wake signals before the brain adapts.
Is melatonin safe long-term?
Low doses may help in the short term, but long-term use disturbs natural production and timing.
Can stopping sleep aids worsen insomnia?
Yes. Rebound insomnia is common if the root causes weren’t addressed.
Final Verdict: Why Sleep Aids Stop Working
Sleep aids stop working because insomnia isn’t a sleep deficiency — it’s a regulation problem.
Lasting sleep comes from restoring:
- Nervous system balance
- Hormonal timing
- Circadian rhythm stability
Once those are addressed, many people find they no longer need sleep aids.
Want targeted support while you fix the root cause? Some people benefit from a non-habit-forming, calming sleep stack alongside better timing, light control, and stress downshifts. If you want to see the option I recommend most